What is Design Thinking?
Design Thinking is a process in which one attempts to transcend an initial level of understanding to tap into alternative strategies and solutions. it involves questioning previously-thought problems, assumptions, and implications. Then, approaching issues in human-centric way through brainstorm sessions, prototyping, and testing. This helps gain an intimate understanding of the clients needs and target users.
Process
There are numerous variations of the Design Thinking measure being used today, which range from three to seven stages. But, they all stem from Nobel Prize laureate Herbert Simon in The Sciences of the Artificial in 1969. While they are largely all the same, we shall focused on the five-stage model proposed by the Hasso-Plattner Institute of Design at Stanford.
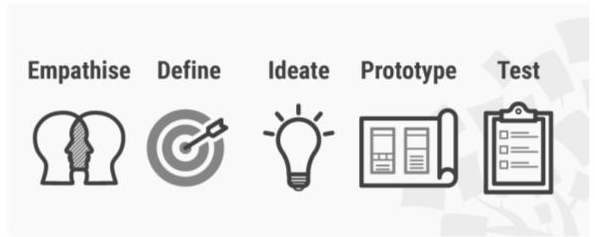
Empathise – Connect with your clients
Define / Characterize – your clients’ needs, their concern, and your bits of knowledge
Ideate – by testing presumptions and making thoughts for creative arrangements
Prototype – to begin making arrangements
Test – test solutions
Design Sprint
GV, or google Ventures, came up with a similar idea and called it Design Sprint designed to offer a “shortcut to learning without building and launching.”
In five days, the Design Sprint will help you to:
1. Understand. Map out the problem and pick an important area to focus.
2. Ideate. Sketch out competing solutions on paper.
3. Decide. Make decisions and turn your ideas into a testable hypothesis.
4. Prototype. Hack together a realistic prototype.
5. Test. Get feedback from real live users.

Rethinking Design Thinking
Design Thinking Takeaway
Design thinking can be a very nuanced subject. But, it’s important to remember that you are not bound to any previously-established version of design thinking–you must make it your own!
| Design Thinking Is… | As Opposed To… |
| Problem-focused | Solution-focused |
| Empathizing before forming conclusions | Jumping to conclusions |
| Comfortable with ambiguity and vulnerability | Discomfort with ambiguity and vulnerability |
| Open to failure | Afraid of failure |
| Iterative and agile | Waterfall |
| Optimistic | Pessimistic |
| Creative problem solving | Doing things the same way as before |
| Dependent on collaboration | Optional collaboration |
| Analytical and imaginative thinking | Critical and analytical thinking |
Get a FREE estimate for your project today.
Our team of experts will review your project and give you a quote at no cost.
Related Posts
Top-Down vs Bottom-Up: Which Automation Approach Should You Choose?
With over 78% companies implementing RPA, it’s time you give it a thought too and to guide you through it, we have a rundown of two…
Top 5 Power BI Hiring Mistakes to Avoid
Building a robust analytics team is essential for modern businesses. Power BI, a powerful data visualization and business intelligence…
You might also like
Stay ahead in tech with Sunflower Lab’s curated blogs, sorted by technology type. From AI to Digital Products, explore cutting-edge developments in our insightful, categorized collection. Dive in and stay informed about the ever-evolving digital landscape with Sunflower Lab.






